THE SPACE ENERGY OPTION
The Space Energy Option is a near term technically feasible and scalable alternative currently available to humanity to divest from fossil fuels while meeting its future energy and climate needs. Supplying inexhaustible baseload power 24/7 throughout the year makes clean energy from space an ideal solution to addressing the climate and energy crises as well enabling a number of other space solutions to address additional crises facing humanity. 10% is considered a minimum contribution by Space Solar Power to meeting the world’s 2050 energy needs.
SBSP
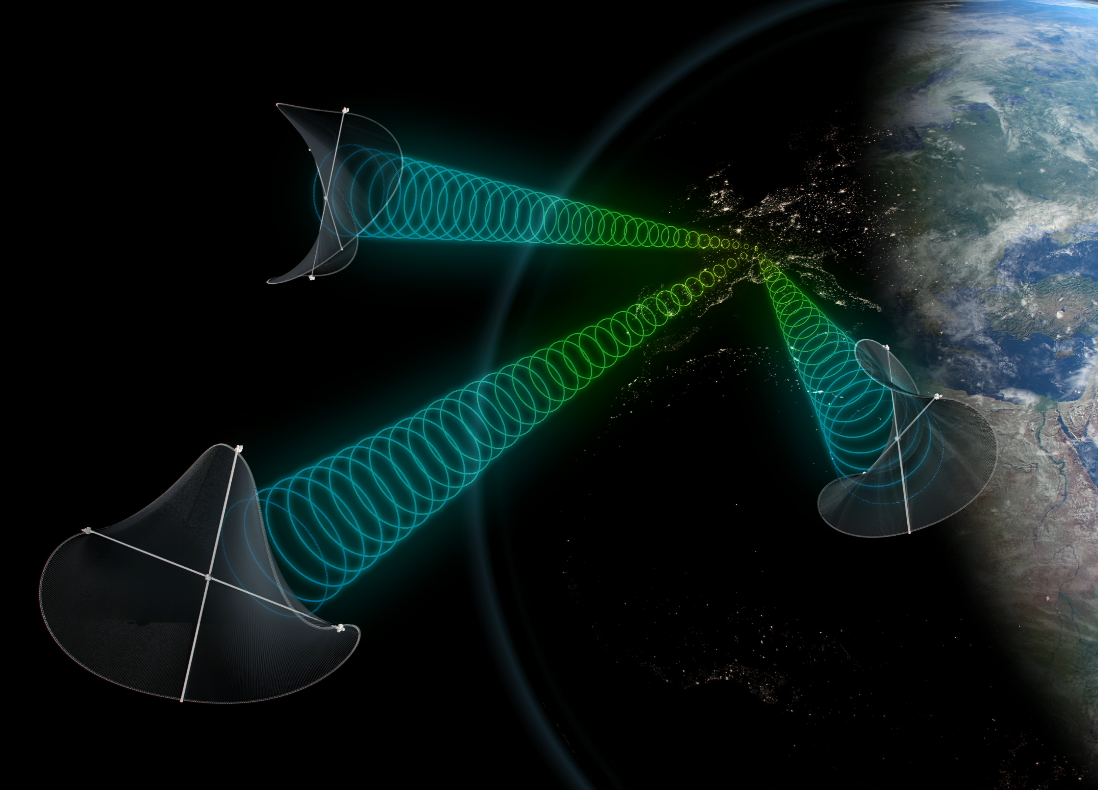
Space-Based Solar Power (SBSP) is a technologically feasible idea that was introduced as the Solar Power Satellite by Peter Glaser in 1968 and patented in 1973. It can supply clean, green and inexhaustible energy to meet humanity’s energy needs.
GREATER EARTH
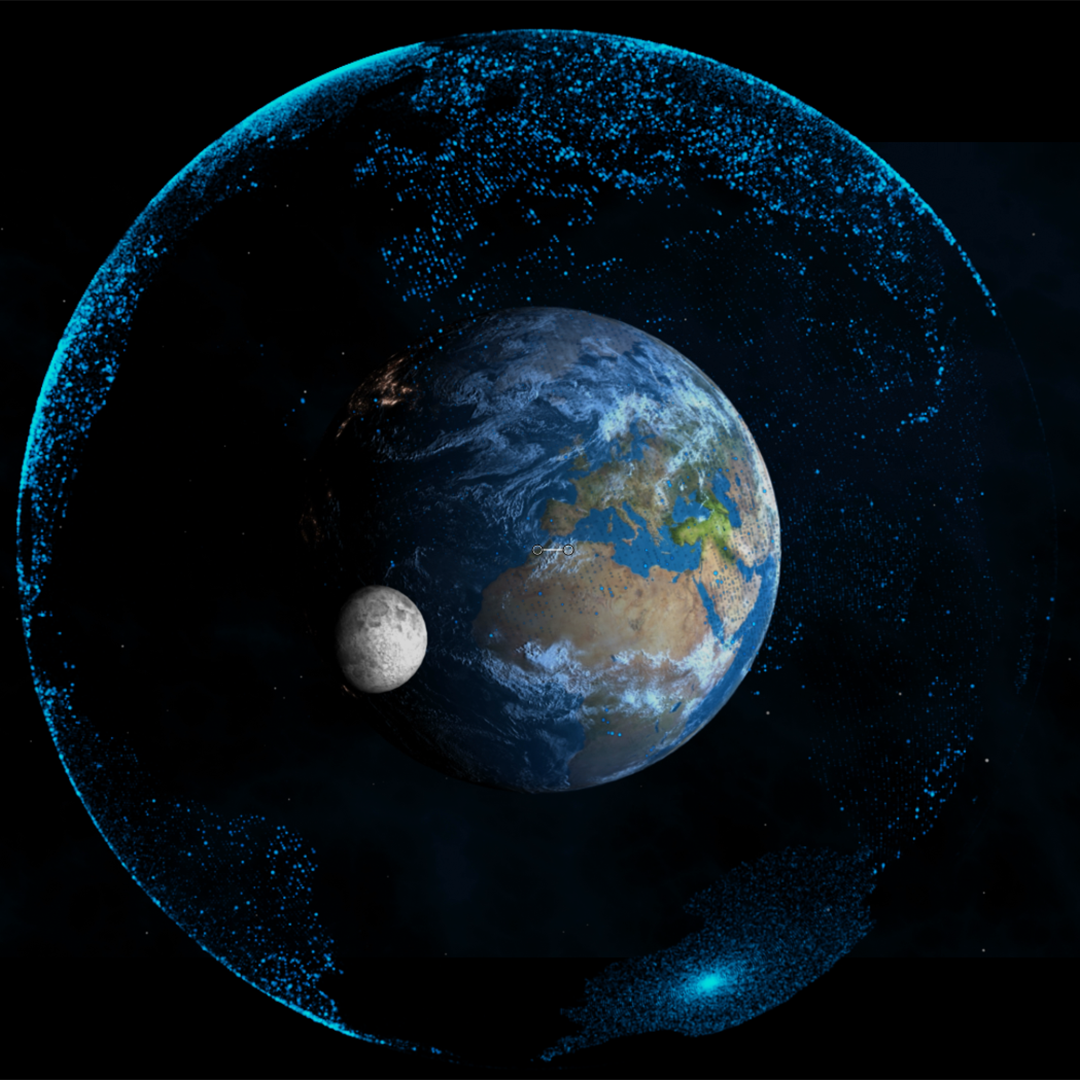
All celestial bodies of significant concentrated mass exert a field of gravitational attraction around their cores which extends to the point of tangential intersection with other celestial bodies. Earth’s gravitational influence extends 1.5 million kilometers in all directions from its center where it meets the gravitational influence of the Sun. This sphere, with a diameter of 3 million kilometers, has 13 million times the volume of the physical Earth and through it, passes some more than 55,000 times the amount of solar energy which is available to humanity on the surface of the planet. In addition to energy, within this sphere are enormous amounts of other resources, including the Moon and occasional passing asteroids.
“We go to Mars to take our civilization there. We go to the Moon to save our civilization here.”
“The Earth is just too small and fragile a basket for the human race to keep all its eggs in.”
“Is a planetary surface the right place for an expanding technological civilization?”
“War and space exploration are alternative uses of the assertive, exploratory energies that are so characteristic of human beings. They may also be mutually exclusive because if one occurs on a massive scale, the other probably will not.”
“If God wanted man to become a spacefaring species, he would have given man a Moon.”
Addressing the major challenges of the 21st century
Meeting these challenges will require strategic innovations in the area of Space-Based Solar Power (SBSP) leading to new jobs and opportunities. Astrostrom’s GE⊕-LPS approach to fabricating Solar Power Satellite (SPS) components on the Moon from lunar materials could reduce the mass-to-orbit needed to be launched from Earth for a SPS by 80% or more. This would favourably impact the logistics, the environmental issues, and the economics of realizing SBSP on a large scale.
From Here to There